Flame Retardant Finishing of Textiles | Mechanism of Flame Retardancy
The human safety has become paramount with the industrialization of the world. So, a massive portion of industrial textile has been involved in developing protective clothing. The main challenge in flame retardant clothing is to make them comfortable to wear as well as environment friendly and non-toxic. To address these challenges, advancements in material science and technology have paved the way for innovative solutions. Among these, 3D textile design techniques have emerged as a game-changer, enabling the creation of multilayered fabrics that enhance both protection and comfort. These techniques not only improve the durability and functionality of flame retardant clothing but also allow for more sustainable and non-toxic material integration. As manufacturers increasingly adopt these 3D textile design techniques, they can tailor fabrics to meet specific safety standards while ensuring that wearers experience greater mobility and breathability. This customization opens new avenues for innovation, allowing designers to create clothing that not only protects against flames but also minimizes the risk of heat stress, a common concern in protective gear. Ultimately, the integration of 3D textile design techniques signifies a forward leap in the quest for safety and sustainability in the apparel industry.
Why is Flame Retardancy Needed?
Flame retardant clothing’s requirements range from situations where the wearer may be subject to moderate heat occasionally during his/her working period to protecting the wearer from severe heat to direct flame. A heat resistant batting is a perfect example of this.
Flame retardancy gives safety from flames in an unsafe area or environment. Generally, firefighters and other emergency personnel need flame retardant garments. In public buildings, upholstery, floor coverings, etc. need protection. There is a lot of military application of flame retardancy.
Mechanism of Flame Retardancy
First, let’s know some important parameters of flame retardant finishing.
- Combustion: Three components, i.e., heat, oxygen, and suitable fuel, are required for this exothermic process. It becomes self catalyzing and continues until the three elements are not depleted.
- Tc (Combustion Temperature): The flammable gases get mixed with the oxygen to create a free radical reaction(gas phase) at Tc. The reaction is highly exothermic and produces a large amount of light and heat.
- Tp (Pyrolysis Temperature): Several chemical changes occur in the fiber at Tp. The chemical changes are irreversible, and it produces non-flammable gas, carbonaceous char, tars, and flammable gases.
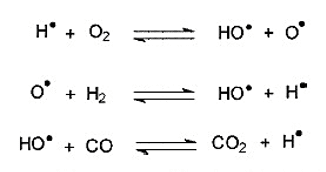
- Mainly the amount of heat generated is the determining factor of a textiles burning behavior. The rate of heat release is the secondary factor.
Now, let’s look at the combustion cycle of fiber.
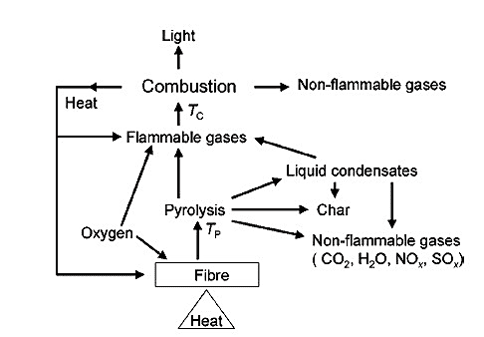
To make a fiber flame retardant, this circle needs to be disrupted. This can be done by the following methods –
An Insulating Layer Around the Fiber Below Tp
Boric acid and its hydrated salts release water vapor and produce a surface that is foamed glassy on the fiber when heated. By this action, they provide insulation from the applied oxygen and heat.
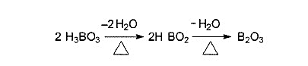
A Heat Sink In or On the Fiber
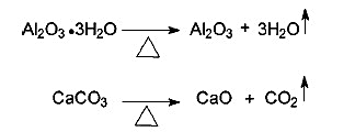
The heat sink is made of thermally decomposable materials through a strongly endothermic reaction. If the reaction can absorb enough heat, the temperature can not go close to the pyrolysis temperature, and so combustion can not occur.
Aluminum hydroxide or Alumina trihydrate and Calcium carbonate are used as coatings in the fiber for this method.
Influencing the Pyrolysis Reaction
Due to this, The production of less-flammable volatiles is more and residual char is less. Phosphorus-containing flame retardants used. During thermal decomposition, they produce phosphoric acid. By cross-linking with hydroxyl-containing polymers, they alter the pyrolysis reaction to produce less-flammable by-products. This is called the ‘Condensed phased’ mechanism.
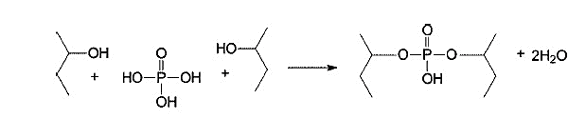
A chemical finish is applied to cellulose to reduce flammability. Some human-made fibers have some additives inside them, which naturally reduces flammability. This property is obtained by adding reactive chemicals in the polymer chains during polymerization or in the solution before spinning.
Ammonium carbonate and Borex are commonly used. During heating, Ammonium Carbonate produces ammonia, water, and Carbon-di-oxide. These gases prevent the oxygen from reaching the fiber. Borax coats reduce the evolution of combustible gases by creating a cover on the fiber surface.
Reactive chemicals are combined with crease-resist resins in the modern flame retardant finishing.
- The material is padded into a solution or dispersion of the mixture of chemicals.
- Then drying and curing is carried out, sometimes washing also.
Key Points of Flame Retardant Finishing
- The color fastness and dyes are both affected by the finish.
- Softening agents are required as the chemicals make the fabric harsh and stiff.
- The cold pad-batch method can be used to reduce the stiffness and also increase the wash-fastness.
Considering Factors of Flame Retardant Finishing
During designing a flame retardant clothing, several things should be kept in mind.
- The textile fiber‘s thermal behavior
- The influence of fabric structure on the thermal behavior
- Non-toxic and smoke-free chemicals selection
- Designing the garment with comfort properties according to its end use
- Ignition source’s intensity
- Availability or supply of the oxygen
Complications of Flame Retardant Finish on Textiles
- Meticulous quality check from end to end, side to side of the fabric is necessary
- Uniform application of the chemical is necessary
- Harsh handle and loss of strength
- Fabric yellowing and change of color
- Careful selection of other substances to combine with flame retardant chemical is necessary
- Toxicity of flame retardant finishes
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between flame retardant and flame resistant?
Flame resistant fabrics are made from inherently non-flammable materials that have built-in flame resistance into their chemical structure. They prevent the spread of fire and will not melt near a flame. They will burn very slowly and, most of the time, self-extinguishing.
Flame retardant fabrics are chemically treated with a particular chemical that provides non-flammability.
How long does flame retardant clothing last?
It depends on fabric material. 100% Cotton fire retardant fabric can last up to 12-16 months. 88/12 Cotton Nylon blend fire retardant fabric can last up to 18-30 months. Synthetic blends fire retardant blends can last up to 2 and a half years to 4 years.
What is durable flame retardant finishes for Cellulose?
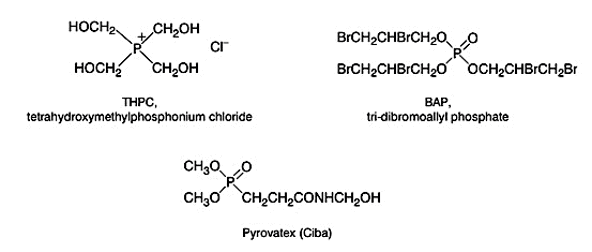
Finishes based on phosphorus and the nitrogen-containing chemical system is the most successful durable flame retardant finishes for cellulose. Tetrakis(hydroxymethyl)phosphonium chloride (THPC) is the main ingredient in this type of finish. It is generated from phosphine, formaldehyde and hydrochloric acid.
In the pad-dry-cure process, THPC reacts with urea and form an insoluble structure on cellulose.
What are the differences between the condensed-phase and gas-phase flame retardant mechanisms?
| Condensed Phase | #SL | Gas-phase |
|---|---|---|
It is based on pyrolysis chemistry | 1 | It is based on flame chemistry |
| As dehydration and carbonization decrease the formation of burnable volatiles, it is very effective. | 2 | Not very beneficial and it changes the fiber properties hugely. |
| It can be applied to mainly cellulose and wool. | 3 | It can be applied to all kinds of fibers. |
| A multi-step process is required for durable flame retardancy. | 4 | Only viscosity control is necessary, so relatively simple. |
| Formaldehyde emits during curing and finishing and phosphorus compounds in wastewater. | 5 | Antimony oxide and organic halogen donators are the primary concern. |
REFERENCES

