Spinning Basics : Yarn Definition | Classification | Types | Flowchart
What is Yarn?
Yarn can be defined as an extensive length of linked fibers formed by attenuation and twist which meets the demand of basic raw materials for the production of textiles, especially in knitting, weaving, sewing, embroidery as well as cable and cord making. The process of manufacturing yarn is called spinning.
Classification of Yarn According to Spinning Technique
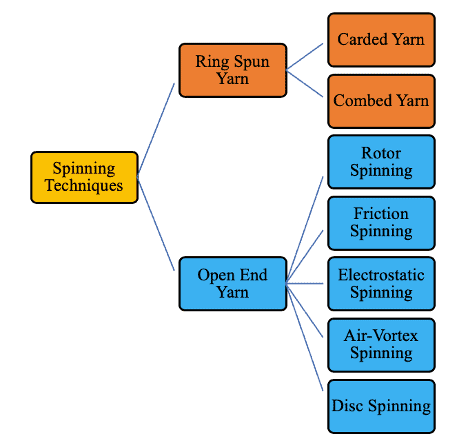
Types of Yarn
Yarn can be classified in accordance with:
| Length | No. of strand | Spinning System | Process Sequence | Fiber Blend | Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Spun yarn (Short Staple & Long staple) 2. Filament yarn (Mono-filament & Multi-filament) | 1. Single yarn 2. Ply yarn 3. Cable yarn | 1. Ring yarn 2. Rotor yarn 3. Air-jet yarn 4. Worsted yarn 5. Woolen yarn | 1. Carded yarn 2. Combed yarn | 1. CVC (Chief Value of Cotton) 2. PC (Polyester and Cotton) | 1. Woven yarn (warp & weft) 2. Knit yarn |
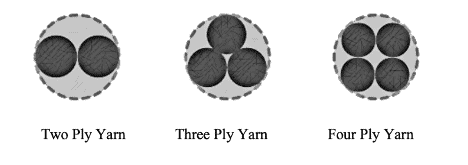
Ply Yarn
A yarn that is not doubled or twisted with another yarn is said to be a single-ply. If two yarns are twisted together and wound in a package then it is called a 2-ply yarn & if three yarns are twisted altogether then it is a 3-ply yarn. Plies are hardened to make yarn resilient for special purposes. In the Denim industry, plied yarns have become significant, especially in piece-dyed fabrics that are expected to sustain an extended stone wash progression.
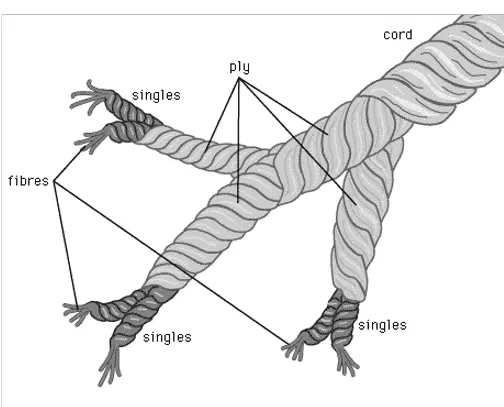
Cable Yarn
A yarn is prepared up of more than two smaller plied yarns warped together is said to be cable yarn. Simple example of a cable yarn is a four-ply yarn where a pair of two-ply yarns are wrapped with each other.
Process Flow Chart for Manufacturing of Carded Yarn
| Input | Process/Machine | Output |
| Bale Management | ||
| Raw cotton | Blowroom | Lap/ Chute |
| Lap/ Chute | Carding | Card Sliver |
| Card Sliver | 1st Draw Frame/ Breaker Draw Frame | Drawn Sliver |
| Drawn Sliver | 2nd Draw Frame/ Finisher Draw Frame | Drawn Sliver |
| Drawn Sliver | Simplex/ Speed Frame/ Roving Frame | Roving |
| Roving | Ring Frame | Yarn (Cops Form) |
| Yarn (Cops Form) | Winding M/C | Yarn (Package Form) |
| Yarn (Package) | Heat set | Yarn (Package) |
Process Flow Chart for Manufacturing of Combed Yarn
| Input | Process/Machine | Output |
| Bale Management | ||
| Raw cotton | Blowroom | Lap/ Chute |
| Lap/ Chute | Carding | Card Sliver |
| Card Sliver | Pre-Comb Draw Frame | Drawn Sliver |
| Drawn Sliver | Super Lap Former | MiniLap |
| MiniLap | Comber | Combed Sliver |
| Combed Sliver | Post-Comb Draw Frame | Drawn Sliver |
| Drawn Sliver | Simplex/ Speed Frame/ Roving Frame | Roving |
| Roving | Ring Frame | Yarn (Cops Form) |
| Yarn (Cops Form) | Winding M/C | Yarn (Package Form) |
| Yarn (Package) | Heat set | Yarn (Package) |
Process Flow Chart for Manufacturing of Rotor Yarn
| Input | Process/Machine | Output |
| Bale Management | ||
| Raw cotton | Blowroom | Lap/ Chute |
| Lap/ Chute | Carding | Card Sliver |
| Card Sliver | Draw Frame | Drawn Sliver |
| Drawn Sliver | Rotor | Yarn |
Differences Between Carded Yarn and Combed Yarn
| Carded Yarn | # | Combed Yarn |
|---|---|---|
| Yarn which is attained lacking combing is said to be carded yarn. | 1. | Yarn which is achieved by combing is denoted as combed yarn. |
| Comparatively the eminence of carded yarn is not up to the mark. | 2. | Combed yarn is superior to carded yarn in terms of quality. |
| Higher percentage of short fiber is present. | 3. | Comber combs out the short fibers. |
| No need to use lap former. | 4. | Super lap former is used here. |
| Comparatively the tensile properties of carded yarn is not up to the mark. | 5. | Combed yarn is superior to carded yarn in terms of strength with same TPI. |
| Irregularity is comparatively higher. | 6. | Combed yarn is more regular. |
Some Important Definitions and Terms
- Lap can be defined as a compress layer or sheet of cotton or wool fiber.
- Sliver is a constituent of loose fibers shaped in carding, combing or drawing and it contains no twist.
- Roving can be defined as a collection of moderately fine fibrous strands, used in the advanced or last course of ‘preparation for spinning’,
- Ginning is the process of sorting the seeds out of the cotton fiber. The supreme Ginning is the extraction of fibers from the seeds without any damage of the fiber.
- Lint: Raw cotton after Ginning is called Lint.
- Linters: The short, fuzzy fibers still attached to the seed after Ginning is called Linters.
Importance of Raw Cotton
The significance of raw materials on the manufacturing cost of a short staple yarn is about 50-75%. This statistic alone is adequate to designate the importance of the raw material for the yarn producer. The yarn quality solely responsible upon the raw materials for about 80 to 90%.
Cotton Fiber Growing Countries
Australia, Burkina, Benin, Turkey, Egypt, Togo, Ivory Coast, USA, Pakistan, Uzbekistan, Brazil, Zimbabwe, China, India, and Mali.
Brand Name of Cotton Fiber
| Brand Name | Country |
|---|---|
| Pima | USA |
| Arizona | USA |
| Raja | CIS |
| Shankar | India |
| Delta | Bangladesh |
Approximate Bale Weight According to Origin of Cotton
| Origin of Cotton | Weight/Bale (Kg) |
|---|---|
| Benin | 225 – 250 |
| Brazil | 247 |
| Burkina Faso | 225 – 226 |
| Ivory Coast | 229 |
| Mali | 226 |
| Pakistan | 152 – 158 |
| Pima (USA) | 220 – 230 |
| Shankar India | 162 |
| Spanish | 230 |
| Tajikistan | 209 – 213 |
| Togo | 236 |
| Turkmenistan | 209 – 230 |
| USA | 229 – 247 |
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Which spinning technique is the most preferable?
To be honest this is very difficult to answer because all of the spinning systems has some unique qualities. If production rate is the concern then open end spinning system is preferable but as long as the yarn quality is concerned there’s no spinning system that can compete against ring spinning system due to its better distribution of twist.
2. Is it a PC or CVC when the ratio of cotton to polyester is 50:50?
Well, if the ratio is same it is called PC yarn because in CVC the portion of cotton has to be higher. In some spinning mills, it’s called TC yarn (Terylene-Cotton) to separate this from the confusion of being PC or CVC. Terylene is another form of polyester.
3. Why lap former is used in combed yarn process?
The main difference between carded yarn and combed yarn is that combed yarn is comprised of mostly longer length of fibers and short fibers are eliminated using comber machine. Comber machine processes laps to comb out the short fibers. If there was no lap former, comber would have to process drawn sliver from pre-comb drawing which is not possible as the feed material for comber is lap only.
4. What kind of spinning wheel is best for spinning coarse fibers?
Wheels with a lower whorl and flyer ratio are great for spinning coarse fiber. In our Ashford Kiwi 3 review, we went deep into this matter.
