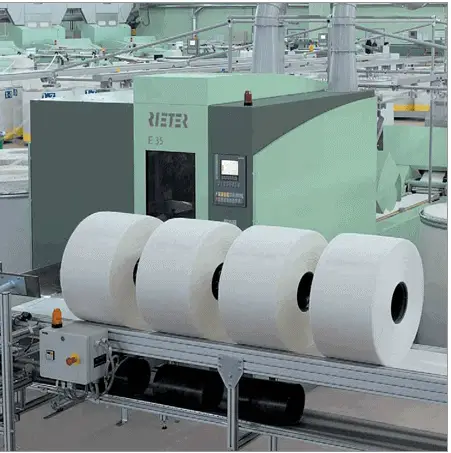
Lap Former : Tasks | Types | Features
To produce superior quality of cotton yarn i.e., combed cotton yarn, we need to employ two more extra machines in our spinning line comparing to our conventional carded yarn manufacturing process. First of all, we need lap formers to produce regular laps and then comber machines to convert those laps into uniform slivers.
A regular process flow chart of carded cotton yarn manufacturing displays that after being processed in carding, the carded slivers are fed into the breaker drawing frame machine. Breaker drawing frame converts them into more regular sliver and later on sends it to the finisher drawing frame machine for extending the quality even higher. But in combed cotton manufacturing system, in between those drawing frames the lap formers and combers are employed.
Why Lap Former is Needed?
Yarns which are made up of longer length of fibres, tend to show less irregularities in subsequent processes. Those yarns are superior in quality and carry lower percentage of hairiness as well. A comber machine provides us such uniform and regular slivers that are free from a predetermined length of short fibres. So, basically for manufacturing such types of greater quality yarn, use of a comber machine is a must in our spinning line.
But before we start to manufacture these uniform slivers in comber which ultimately lead us to craft extra-ordinary yarn, we need to produce a number of uniform laps as well. To produce those laps, there the lap formers come into action.
As the comber machine is unable to process the drawing frame slivers directly and relying on lap feeding system only, introduction of the lap former machine becomes mandatory. Besides, lap feeding system helps the comber to comb it better and efficiently in comparison to hypothetical sliver feeding system.
Lap Former: The lap former has the charge of developing the laps that is engaged to feed the comber machine. The laps are achieved through combining or doubling a definite number of slivers from breaker drawing passage such as- 16 to 32 doubling or at times even as much as 64 doubling.
Tasks of a Lap Former
- Diminishing the irregularities such as – thick and thin places
- Producing regular and even lap for comber machine
- Declining the fibre damage throughout the processing
- Parallelizing and straightening the fibres in laps
- Lessening the chances of upright fibres waste
Brands of Lap Former
- Trutzschler, Germany.
- Rieter, Switzerland.
- Toyoda, Japan.
- Murata, Japan.
- Lakshmi, India.

Categories of Lap Former
There are two types of lap formers available in our spinning mills-
Conventional lap former: Here two machines are used to produce a lap.
Sliver Lap Former
Ribbon Lap Former
Modern Lap former: Here, state-of-the-art technology is used to produce laps from breaker drawn slivers.
Super Lap Former
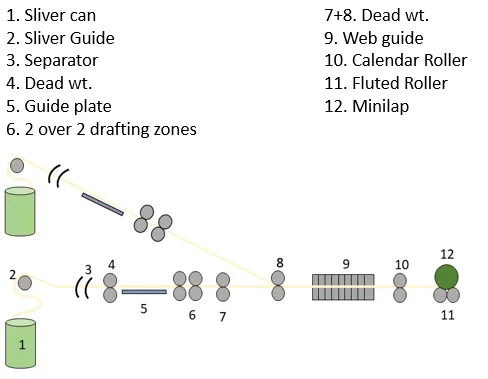
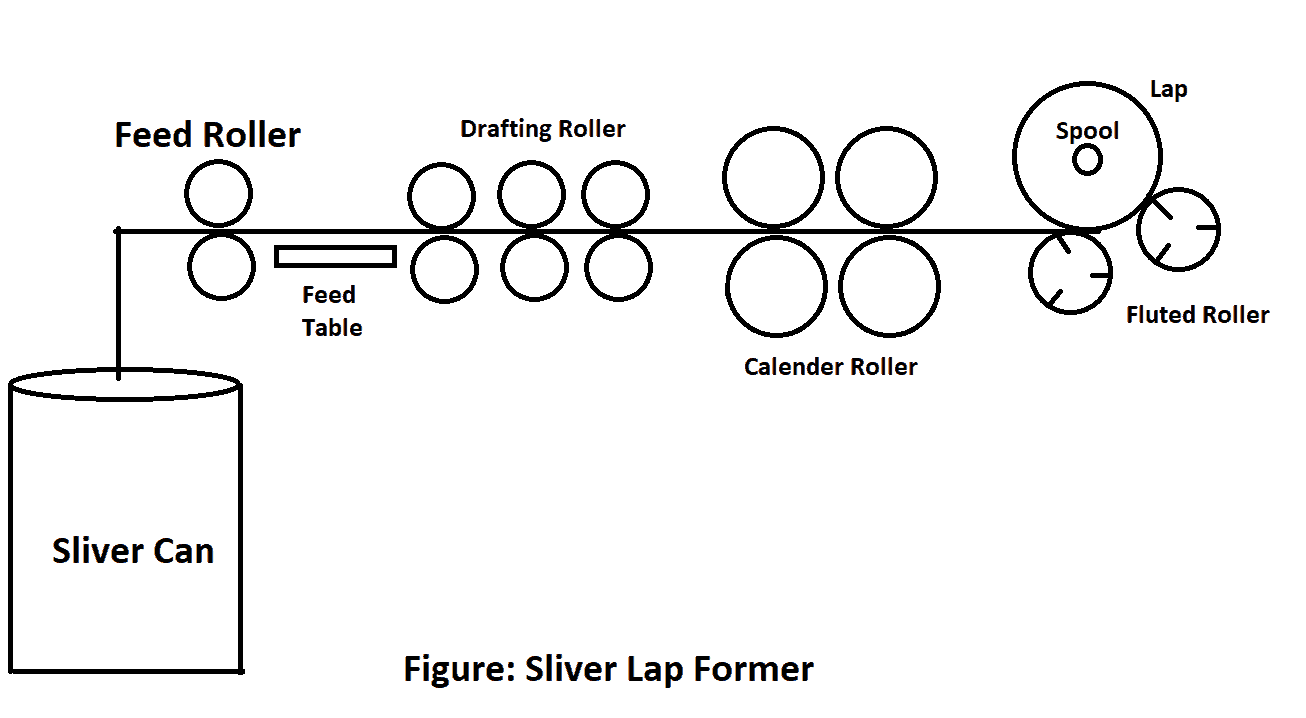
Sliver Lap Former
- Individual sliver goes through the guide plate at the rear of the machine.
- Then the slivers are passed over a distinctive spoon.
- The slivers are led through a V-shaped feed table that links them to the neck.
- The slivers are then passed into 3 pairs of roller designs.
- Because of the draft, the fibers are finally sorted, straightened and paralleled.
- Afterwards when, the lap sheet runs through two pairs of calendar rollers that compact it into a sheet.
- During winding on the spool, tremendous pressure is applied to the bobbin so that a long compressed lap can be achieved.
- When the appropriate lap length is already rolled to the spool, the Lap Stop Motion stops the machine immediately.
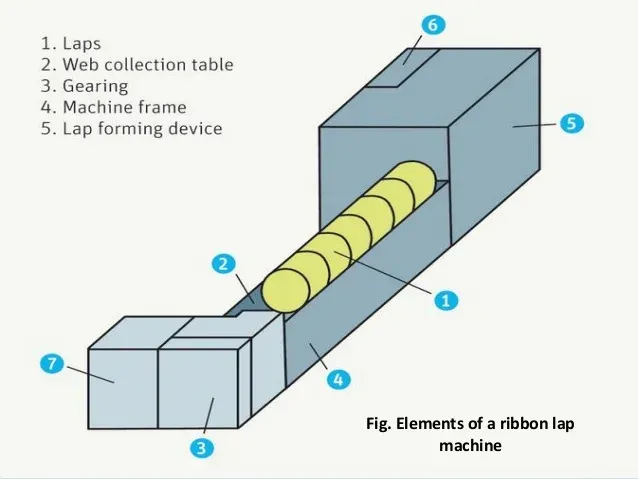
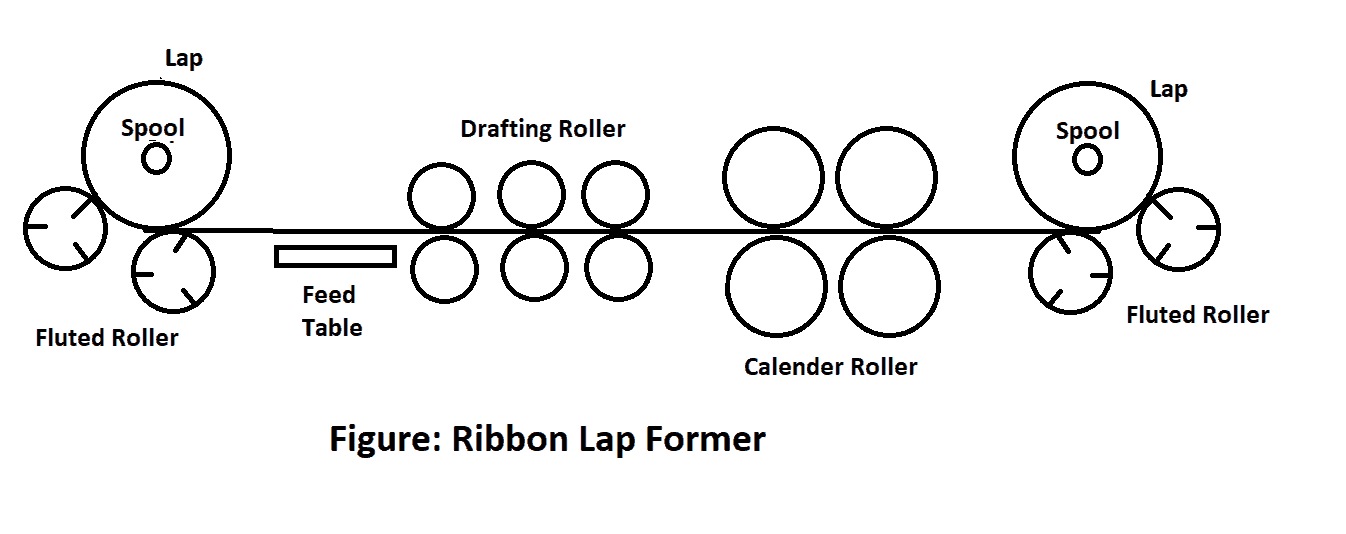
Ribbon Lap Former
- The process starts with creeling. You already know that the material ended up here from the sliver lap former. Before feeding them into the drafting rollers, the laps are opened first.
- The true purpose of this unit is to increase the linear density (wt/length) and consistency of the lap acquired from the last machine (Sliver Lap Former).
- Here, six to eight laps are served as input. While the output material features the same width, the thickness gets increased – thanks to the doubling and drafting process.

- Mostly, 3 over 3 or 4 over 4 drafting arrangements are activated here.
- When the drawing process is complete, we get a material that’s in a web form. Then, it goes through two more points – the deflector plate’s web table and calendar rollers.
- At this stage, compacting is done by the calendar rollers (two pairs).
- As a result, we’ll get our desired comber lap. Here, it’s wound on bobbins (spool type). For achieving a lap that’s compact, 2 fluted rollers are engaged here.
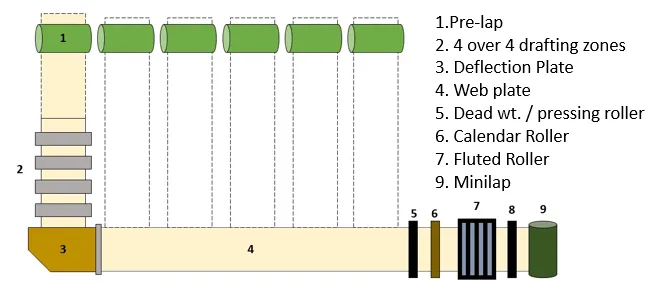
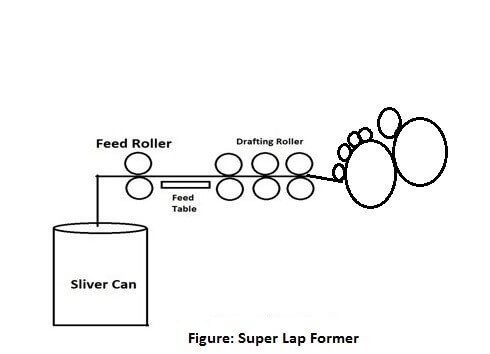
Super Lap Former
- Super lap former machine is being used in contemporary system.
- The purpose of employing this machine is to upsurge the weight per unit length of comber lap.
- There are three creels on the machine, three different zone arrangements and three diverse feed plates in this machine. Here, 48-60 slivers (in each creel 16-20 slivers) can be fed at a time.
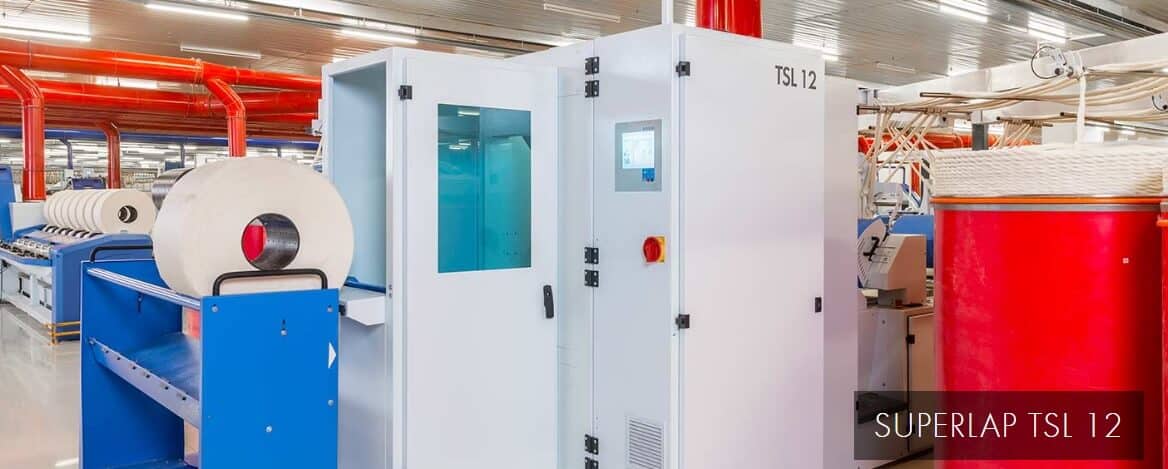

- The slivers passed through the drafting system.
- After drawing the webs are led through the pairs of calendar rolls and along a table where they are superimposed, compressed and calendared into a compact lap.
- Stop motions are set up to all the rollers comprising the calendar rollers and an indicating light is fixed there.
- Here, doffing of full laps and threading are fully programmed.
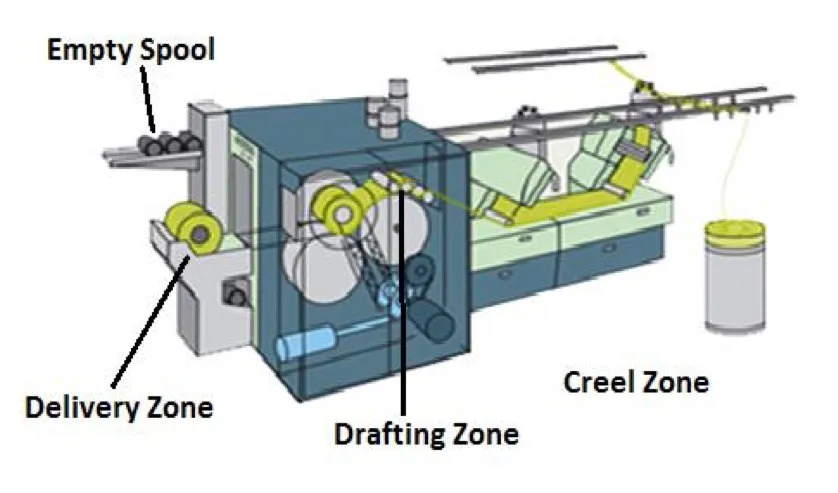
Additional Features of Super Lap Former
- Automatic weight per unit length adjuster
- Auto Doffing for full laps
- Automatic Stop Motion for –
Full/ Partial Doffing
Sliver Breakage
Roller Lapping
- Automatic lap carrying device
- Lap length measuring unit
- Indicating lights for different fault location
Technical Specifications of Rieter E35 and E32 Model Lap Former
| Sl | Parameters | E 35 | E 32 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Production | Up to 520 kg/hr |
Up to 350 kg/hr |
| 2 | Input Weight | Maximum 140 ktex |
Maximum 140 ktex |
| 3 | Lap Hank | Up to 80 ktex |
Up to 80 ktex |
| 4 | Lap Weight | Fixed 25 kg |
Up to 25 kg |
| 5 | Lap Width | 300 mm |
300 mm |
| 6 | Delivery Speed | Up to 180 m/min |
70-140 m/min |
Dimension of Sliver Lap
GSM = 52–72 g/m
Width = 220–301 mm
Diameter = 505 mm
Weight up to = 26 kg
Production Calculation of Lap Former:
PARAMETER:
- Delivery Speed : 95 m/min
- Lap Weight : 70 gm/m
- Efficiency : 85%
Production = (95(m/min)×60(hr)×0.85(Efficiency)×70(gm/m)) / (1000 (kg))
= 339.15 kg (answer)
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why do we use ribbon lap former machine?
The main purpose of ribbon lap former machine is to form a greater size lap from smaller sizes of mini laps that are delivered from sliver lap machine.
2. Is lap former really necessary for producing superior quality yarn?
Well, quality of yarns mostly depend on the fiber’s staple length and length uniformity of the fiber. To produce greater quality of yarn, elimination of shorter fibers are compulsory and to do so, utilization of comber machine is essential. Since comber machine relies on lap feeding system and the previous machine produces drawn sliver… that is why the lap former is extremely essential for producing highest quality yarn.


