Garment Dyeing with the FLAINOX Rotary Dye Extractor
Garment dyeing is one of the hottest prospects in modern times. Since its inception, it’s attracted lots of interest. Today, I would like to share some info based on my experience working in a reputed garment dyeing facility.
In the world of dyeing/finishing, FLAINOX is a renowned name. Being founded in 1968, the company is operating for over 40 years with its state-of-the-art manufacturing plant and impeccably reliable machinery.
FLAINOX is considered as a specialist when it comes to the construction of rotary dye-extractors. Their machine is used for fiber dyeing, yarn dyeing, and special finishing machines.
Flainox Rotary Garments Dye-extractor
This brand is popular for its continuous evolution and sustainable approach in developing its technology, and this machine is a prime example. Let’s talk about some of its features.
The FLAINOX NRG HT model is a rotary machine for dyeing garments, socks, and seamless at a high temperature(135°C) with utmost reliability. High thickness AISI 316/L stainless steel is used in its construction to provide safety and durability.
Furthermore, the machine provides an Automatic Reintegration Function at minimum(ECO LEVEL) to ensure safety.
Machine Parts
- Dyeing Vessel
Bulk dyeing machine has 3 baskets in the dyeing vessel. However, the sample dyeing machine has 1 basket.
- Tanks
The machine has two tanks.
- Heat Exchanger
An integral part of any dyeing machine. The heat exchanger allows the heat from one medium (say liquid/gas) to another medium without having to mix them together.
- Dye-Bath Analyzer
This is used to record the progress of the color on the fiber and print the curve for later comparison.
- Water Flow Speed Meter
To maintain the water flow speed.
- Other Parts
- Filter
- Motors
- Monitor
During dyeing, the vessel can be rotated both clockwise and anticlockwise, as needed.
The rotation time is 45sec clockwise, 45 sec anticlockwise, and there is the 5-sec stationary time between them.
Setting for Pre-heating
This is a necessary stage in most of the dyeing processes. It is done to make the garments dimensionally stable after dyeing. Pre-heating is done for approx. 12 seconds at 160°C.
Garments Dyeing Flow Chart
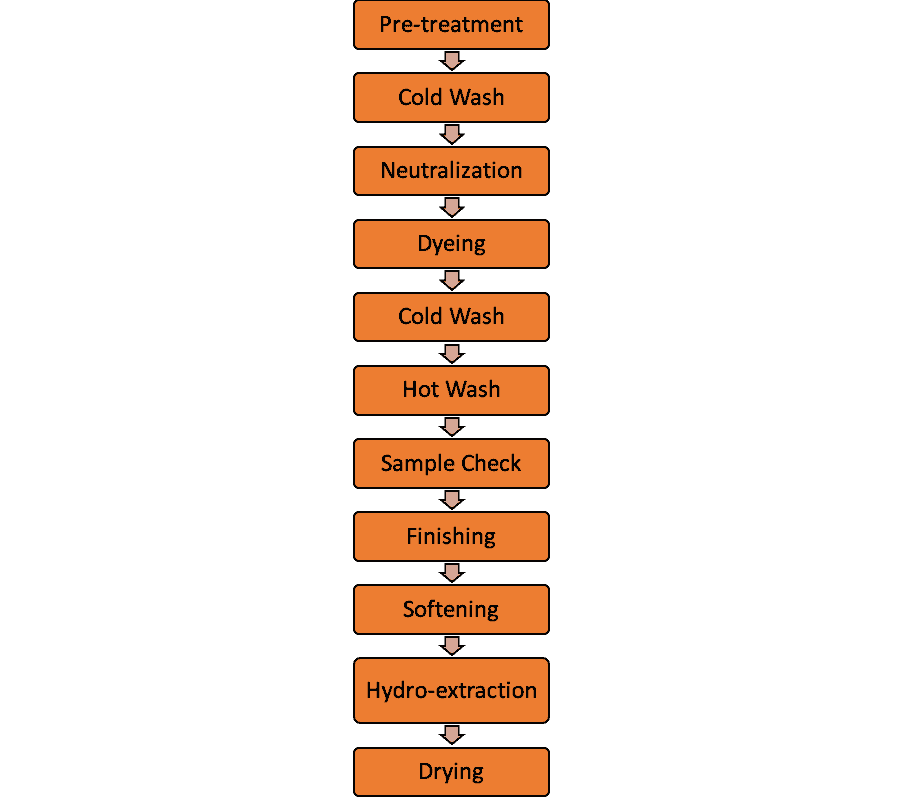
Pre-Treatment Recipe
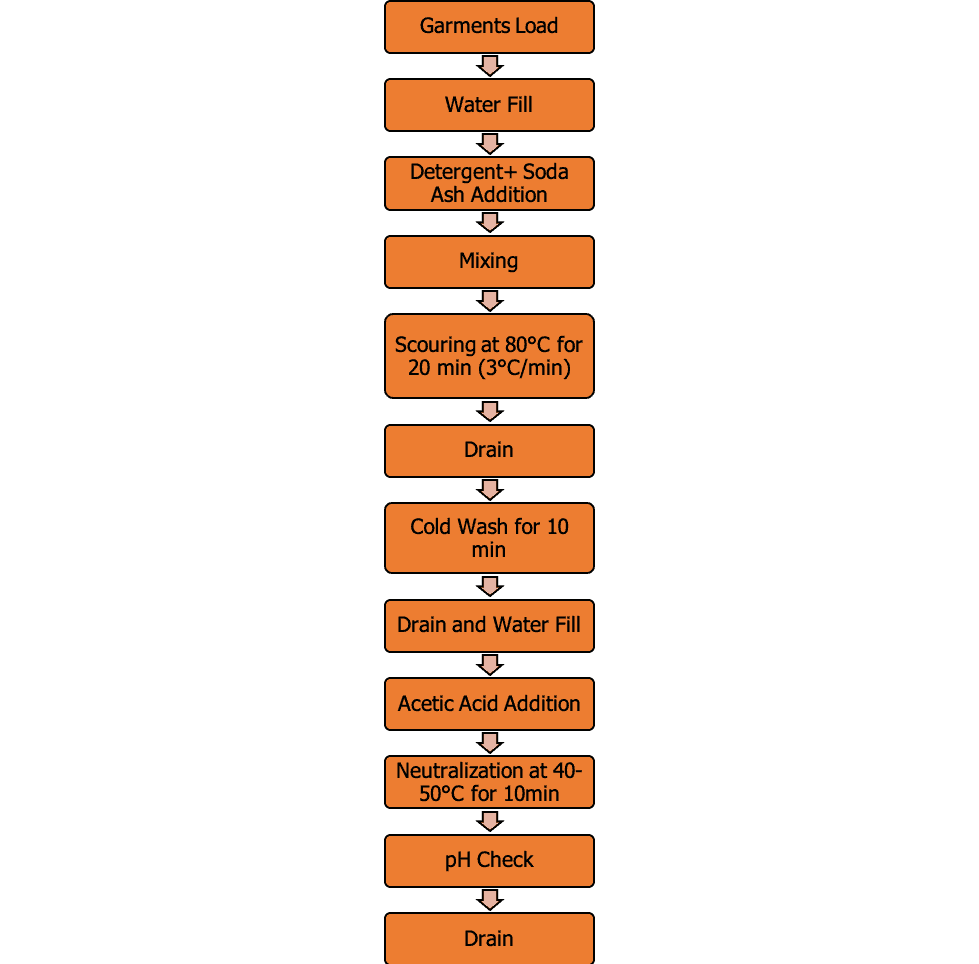
Any treatment, that is done prior to dyeing is known as pre-treatment. It’s done to mainly remove dust, dirt, and oil from the surface as well as to achieve the desired level of whiteness. After all, we cannot hope to achieve good dyeing without preparing the fabric properly!
- Detergent (Tissococyl RC-09)
- Soda ash
- Temperature- 80°c (3°c/min)
- Time: 20 min
- M:L – 1:20
Neutralization Recipe
This process is done to remove extra alkali from the fabric surface which was used during the pre-treatment process.
- Acetic acid
- Temperature: 50ºC
- Time: 10min
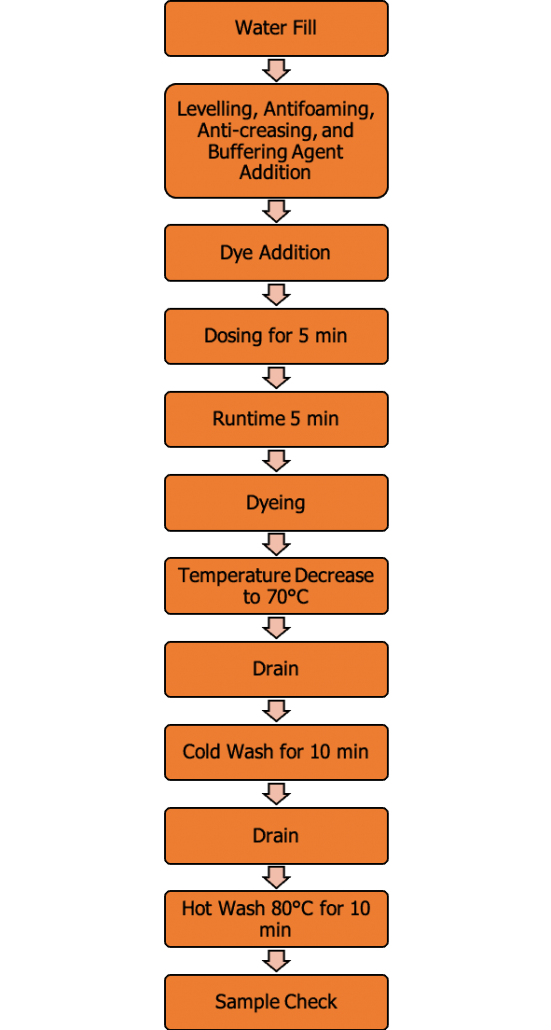
Dyeing Parameters
Gradient and Time
| Parameter | Light | Medium | Dark | Extra dark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | 30 min | 45min | 60min | 90min |
| Gradient | 0.5°C/min | 1°C/min | 1.5°C/min | 2°C/min |
Chemicals
- Levelling agent (Univerdine MC-PA, Crosscolor-PES, 2g/l)
- Anti-creasing agent (Rubine HTC)
- Buffer (Albatex AB 45. 2g/l)
- Antifoaming agent (Albaflow FFC, 2g/l)
Temperature for Different Substrate
| Nylon | Polyester | CDP |
|---|---|---|
| 98°C | 130°C | 110°C |
Things You Should Know for Garment Dyeing
Here is some additional information we should know:
- Preventing Unevenness
1:20 liquor ratio can be used to prevent unevenness during dyeing.
- Single Bath Dyeing
For single bath dyeing of nylon and PES, dyes for polyester are added first at 35°C, and when the temperature reaches 80°c, dyes for nylon is added. Dyeing is carried out at 110°c.
- Double Bath Dyeing
In the case of double bath dyeing, PES is dyed first, and then nylon dyeing is carried out. Finally, fixing and softening are carried out.
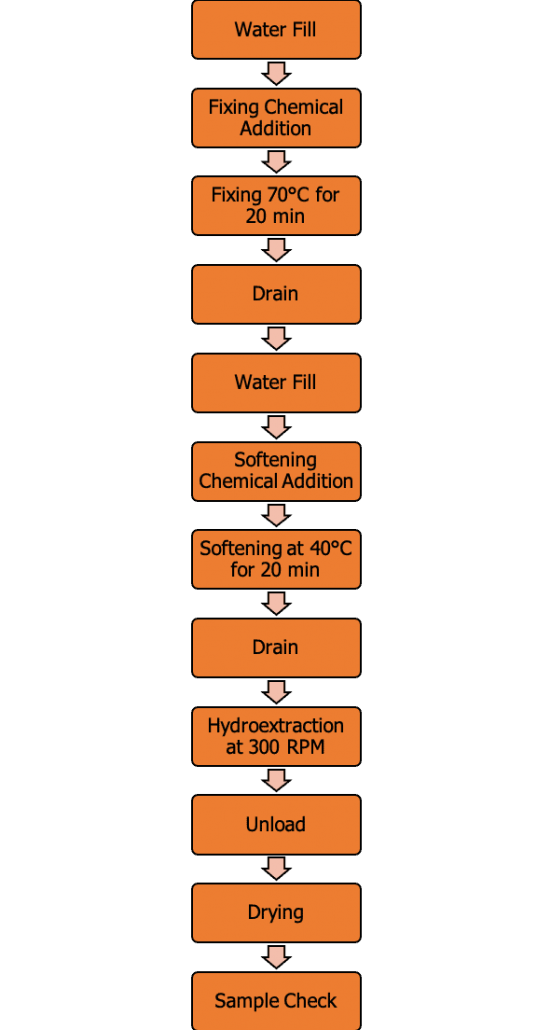
Fixing Recipe
This is a very important step. After dyeing fabric is left with unfixed dyestuff on the surface. And if it becomes the final product it causes color migration while washing. Therefore fixing is done to improve color fastness.
Fixing agents that is used are:
- Fixing agent (Renfix PAK)
- Temperature: 70°C (3°C/min)
- Time: 20 min
Softening and Finishing Recipe
- Softening agent (Tubingal GSI, Feron ICE, Tripal MM)
- Temperature: 40°C
- Time: 20min
Different Blend Dyeing Processes
- Single Part Dyeing
Either nylon or PES is dyed.
- Double Part Dyeing in One Bath
First the dyes for PES is added in room temperature and when the temperature reaches 80°C then dyes for PA is added. Runtime at 80°C for 10 min. At last temperature is increased to 110°C Dyeing is carried out.
- Double Part Dyeing in Two Baths
After pre-treatment first PES is dyed first and shade matching is carried out. Then Nylon is dyed. At the end, fixing and softening is carried out.
Stripping
- Chemicals: Hydrose and Caustic, Levelling and antifoaming agent.
- Temperature: 98°C (1°C/min) – For CDP+NYLON or Nylon
- Time: 30 min
Machine Washing
Chemicals
- Hydrose, caustic and detergent
Process
- For PES: At 120°C, add hydrose and caustic first, and then add levelling and antifoaming agent.
- For Nylon: At 98°c, add Hydrose and Caustic first, and then add levelling and antifoaming agent.
- Runtime: 30-60 min depending upon shade
- Detergent wash at 80°C for 10 min
- Neutralization at 50°C for 10 min
Machine Hot Wash
- Chemical: Soaping agent (Eriopon OS)
- Temperature:80°c at 3°c/min gradient
- Time:10min
A Typical Cotton Garment Dyeing Process with FLAINOX Dyeing Machine
Pretreatment Process
Cellulosic Garment Dyeing Process
Fixing & Finishing Process
Dyeing Faults
Keep in mind the following dyeing faults might be visible after dyeing with this machine.
- Crease mark
- Snagging
- Yarn missing
- Folding mark
- Hem damage
- Naps
- Broken stitch
- Hole in fabric


