Types of Fabric Dyeing Machines: Working Principal & Properties
Recently, during a class our honorable Prof. Dr. Mustafizur Rahman Sir brought up a very interesting topic. He discussed about the ‘Global Competence’ of the Textile Engineers that our country is producing. Many important points were made by him.
Among them the most important was the ‘Basic Understanding of the Subject’ & ‘Our Naïve Approach’ towards it.
So, here I am trying to gather all necessary things that are thought to be ‘Basics’ in a series of posts.
I will start with the fabric dyeing machines.
Fabric Dyeing Process
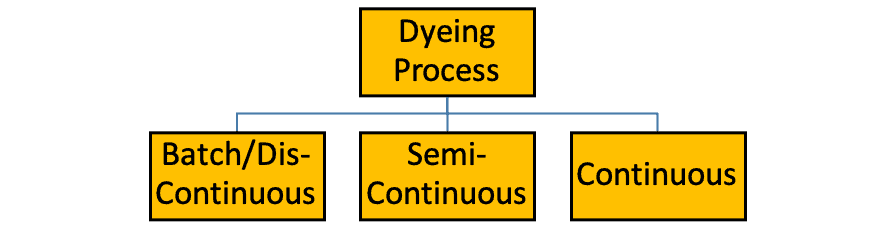
Before we get into the technical side of it let’s apply our common concepts first. We watch various TV commercials everyday which claim that their products are produced without the use of the hand.
What they mean is from start to finish no manual material handling is needed i.e. they feed the Raw Materials as input & receive the final product as output without any intervention. This is called Continuous Process & Batch/Dis-continuous project is exactly the opposite. In a semi-continuous process, both concepts are implemented.
The above-mentioned concept can also be applied to Dyeing processes as well. If we consider fibers as input & garments as output then we would have to agree that the overall process is a Batch process.
Batch/Dis-Continuous
- Here a certain/known amount of material/fabric is brought under repeated contact with dye liquor & then transported to carry out the subsequent processes.
- This type of machine allows processing in rope form (e.g. winches, jets, etc.) or in open-width form (e.g. jigger)
- For knit dyeing, this process is used almost everywhere in our country
Semi-Continuous
- Here dye solution is applied by padding & then it’s batched/stored in certain conditions for fixation.
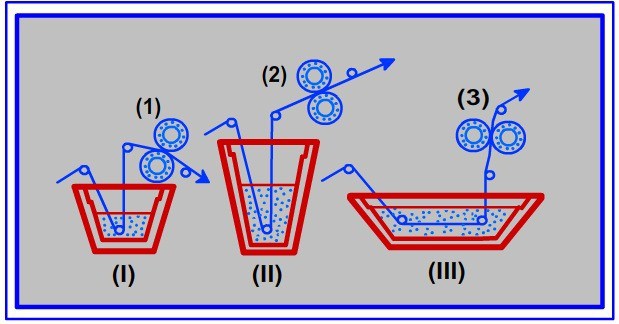
- Padding can have the advantage of high dye yield. Padded goods are usually “batched”– wrapped in plastic and left for some period of time for the dye to attach to the fiber, or steamed to fix the dye quickly.
- Padding methods are sometimes used for other textile processes such as bleaching. & then it’s batched/stored in certain conditions for fixation.
- The subsequent processes (washing, drying, etc) are done afterward.
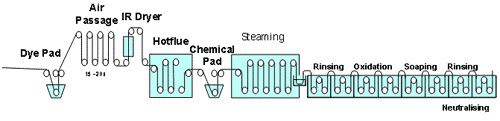
Continuous
- This type of process is aimed at higher production.
- Here dry undyed fabric enters at one end & dry colored fabric leaves at the other end. This is why it’s also called dry-to-dry
- All the units for example padding, steaming, washing, drying, etc. are just set one after another
A typical diagram is shown below:
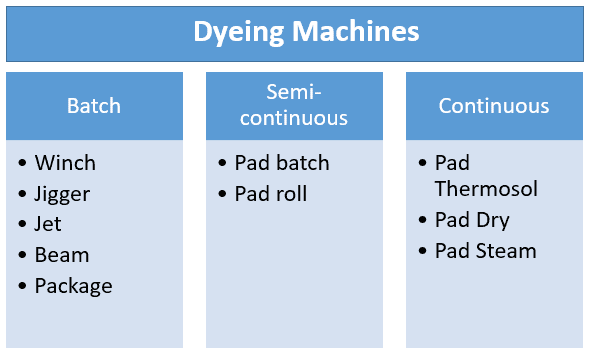
Fabric Dyeing Machines
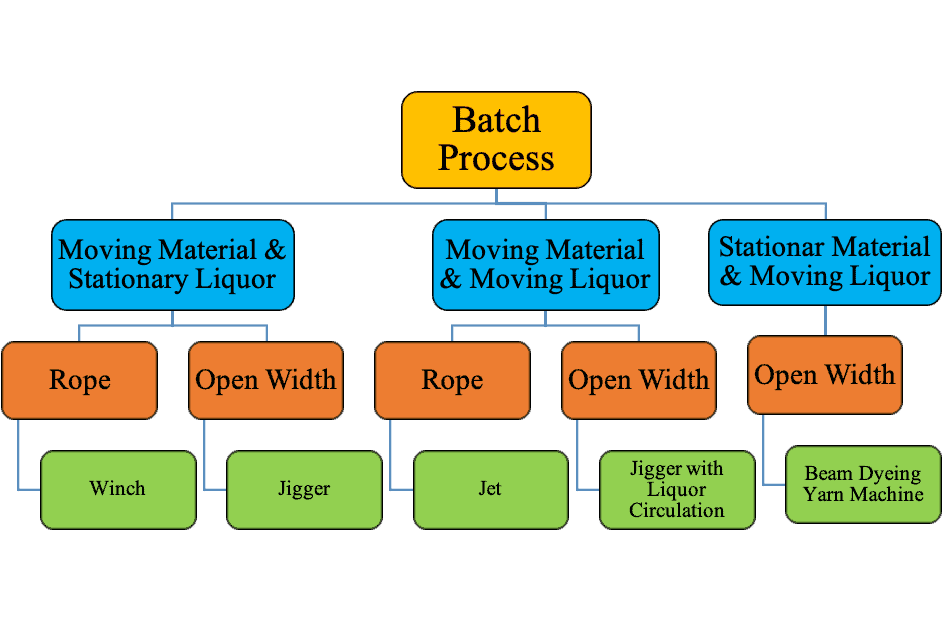
Fabric dyeing machines are the type of dyeing machine that’s employed the most. Here is the classification of fabric dyeing machines according to their working process –
Principles of Batch/Discontinuous Machines
In the following chart the principles, form in which they are fed into the different Batch machines are given –
Why Rope form is used/what are the advantages of rope form processing?
- It’s the easiest method of processing.
- Handling & Storage is easy.
- Ease of transportation as it can be transported to virtually any distance and any direction by passing it through circular guides.
- The fabric doesn’t undergo much tension widthwise which is a very significant factor as the winch machine is extensively used for knits that have low dimensional stability.
Now, I will try to discuss different fabric dyeing machines very shortly.
Winch/ Beck Dyeing Machine (Moving Material and Stationary Liquor)
Why it’s called winch ?
A horizontal rotor/reel is used to circulate the fabric endlessly. This rotor/reel is known as winch. The winch maybe elliptical or circular in cross-section. The elliptical winches exerts minimum tension but high mechanical action by giving long & short folds when the fabric rotates.
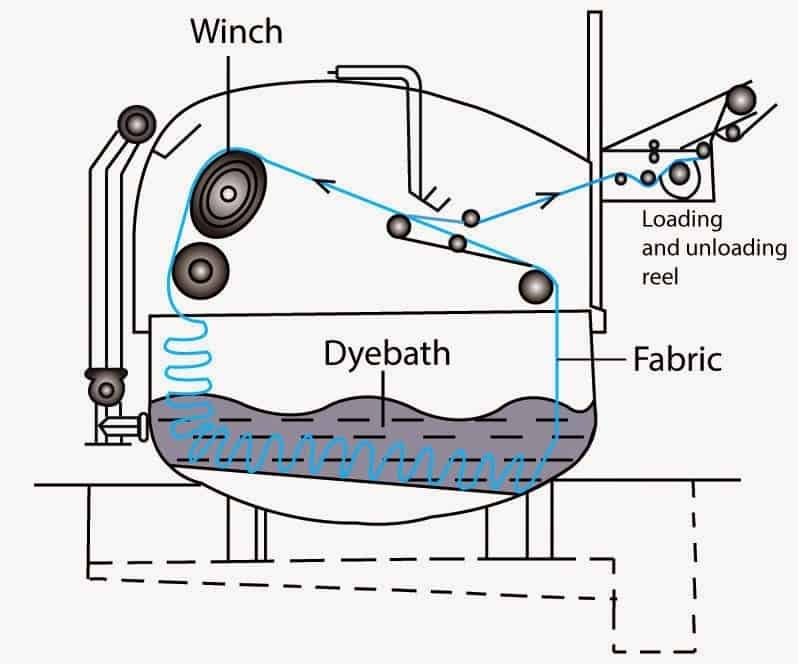
- We can learn from the chart that the fabric moves in Rope Form through the dye liquor (stationary) repeatedly.
- It’s used for all processes including scouring, bleaching, dyeing, washing-off & softening.
- The liquor ratio is typically about 20:1 but for small winches it may be as high as 1:40.
- The most modern machines have the winch drive which can spped upto 500 m/min depending on the fabric properties.
- The nominal chamber capacities are 100Kg, 200Kg & 250Kg.
- Operating temperature can be extended upto 140 Degree Celsius (for closed systems).
- A number (1-40) of endless ropes or loops of fabrics of equal length (about 50-100m) are loaded with much of their length immersed in folded form inside the dyebath.
- The rate of dyeing is controlled by the number of fabric cycles in a given time.
Advantages of Winch Dyeing
- Simple construction & therefore economical to purchase and operate.
- Suitable for all types of fabric specially lightweights.
- It imposes much less tension than Jigger so it’s suitable for delicate fabrics.
- Scouring efficiency is high due to greater mechanical action caused by constant reformation of lengthways folds.
- Tubular knitted fabrics are scoured & dyed extensive because of the low tension.
- Crimps are developed due to greater mechanical action & low tension.
- The dyed fabric is thicker with fuller handle, more fabric cover & better crease recovery.
Disadvantages of Winch Dyeing
- The temperature varies in different parts. The heating unit is present only in one compartment so when the fabric leaves that compartment it cools & then re-enters. So, for temperature sensitive dyes it’s a major drawback.
- Excessive movement may lead to undesirable felting in Wool fabrics.
- The fabric is irregularly piled & uneven dyeing may occur unless suitable dyes & levelling agents are used.
- Due to high liquor ratio, dye exhaustion is poor & considerable amount of dye remains in the bath which hampers the economy.
- Formation of running creases during dyeing may not be removable even after stentering.
- Elongation & deformation may occur due to longitudinal tension.
- Longer rope may cause entanglement at the bottom.
Jigger Dyeing Machine (Moving Material and Stationary Liquor)
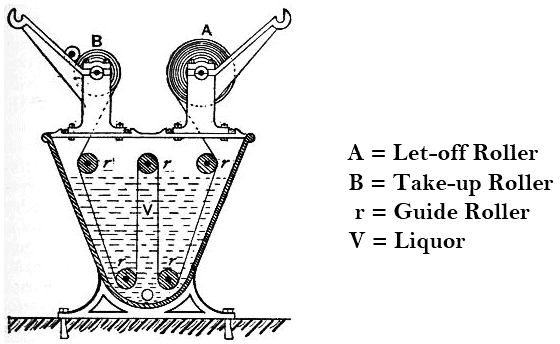
- The jig/jigger is one of the oldest type of machine for dyeing woven fabrics which must not be creased during dyeing, e.g. most taffetas, satins, poplins, ducks & suiting. It’s not suitable to dye knit fabrics as high tension is exerted on the fabric.
- The machine operates with low material to liquor ratio (1:5 to 1:6).
- Here the fabric moves in open width through dye liquor.
- It consists of a V-shaped trough (100 – 150 gallon capacity) with two rollers called draw rollers fitted above it.
- When all the cloth passes through liquor from one roller to another, the passage is called an “end” or one “turn”. An even number of ends are given based on the size of the roll/batch of cloth, time required for one end (usually 10-15 min), and on the depth of shade being dyed etc.
- When the second draw roller (take-up roller) is full the direction of the fabric movement is reversed so the take-off roller becomes the let-off roller & the let-off roller becomes the take-up roller after each turn.
- To ensure that complete length of the fabric is immersed 4-5 metres of cheap end-fabric are sewn to each end of the roll.
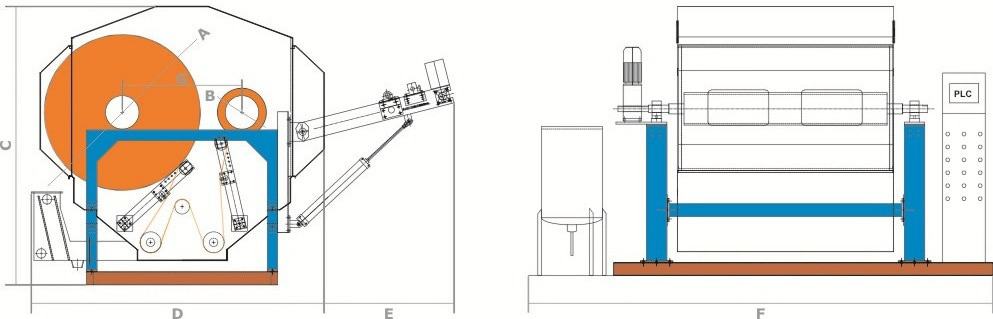
- To ensure that the cloth passes through the liquor at uniform speed, the speed of the let-off & take-up roller is kept constant which is about 40-100 m/min.
At speed in excess of around 110 m/min, on small diameter rolls, the dye liquor may be thrown out of the rotating roll by centrifugal force.
Why the let-off & take-up speed should be kept constant?
- The cloth must be wound on roller with coincident selvedgese. no part of the selvedge should be coming out of the roll. This creates a severe problem in Vat dyeing. When a part of the selvedge comes out of the roll during faulty winding leuco vat dye present in the exposed selvedge gets oxidized & when it re-enters the dye solution this portion of the selvedge picks up more dye than the body of the fabric. As a result, the selvedge is dyed deeper than the body of the cloth.
- In order to avoid tailing effect (gradual lightening of shade) the dye has to be added in an even number of portions.
- Dye adsorption & diffusion takes place at dwell periods on the roll, not at the dye bath.
The Factors for Controlling Dyeing Are –
- The amount of liquor held in the interstices of the fabric.
- The exhaustion of the liquor in time between successive immersion.
- The degree of interchange of exhausted dye-liquor with fresh dye-liquor during each immersion.
Advantages of Jigger Dyeing
- The machine operates with low material to liquor ratio (1:5 to 1:6) so less energy & chemicals are needed.
- Fabrics which are prone to creasing in rope form can be processed in this machine.
Disadvantages of Jigger Dyeing
- Suitable only for the materials in which the dye do not exhaust well as the machine operates with low liquor ratio.
- Knits, crepes ,flat crepes ,net fabrics and elastomeric warps other tension sensitive fabric can’t be dyed in this machine
- It exerts high tension in warp-ways so lengthways extension may be as high as 5% which leads to lengthways shrinkage of the fabric in washing, lowering of warp crimp & reduction of fabric width.
- Special care needs to be taken to ensure that the tension exerted on the fabric is constant & cloth is passing through the liquor at uniform speed.
- In textile preparation due to the swelling and dissolution of size the fabric becomes slippery and unstable in roll form.
- The low liquor ratio makes washing-off difficult.
- There is little mechanical action in a jig machine and it is less suitable where vigorous scouring is required before dyeing.
- Moiré effects or water marks may arise on some acetate and nylon fabrics because of pressure flattening the structure of the rolled fabric.
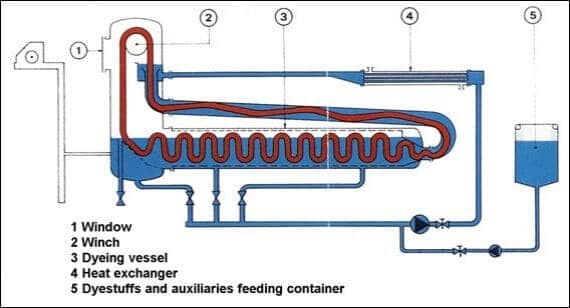
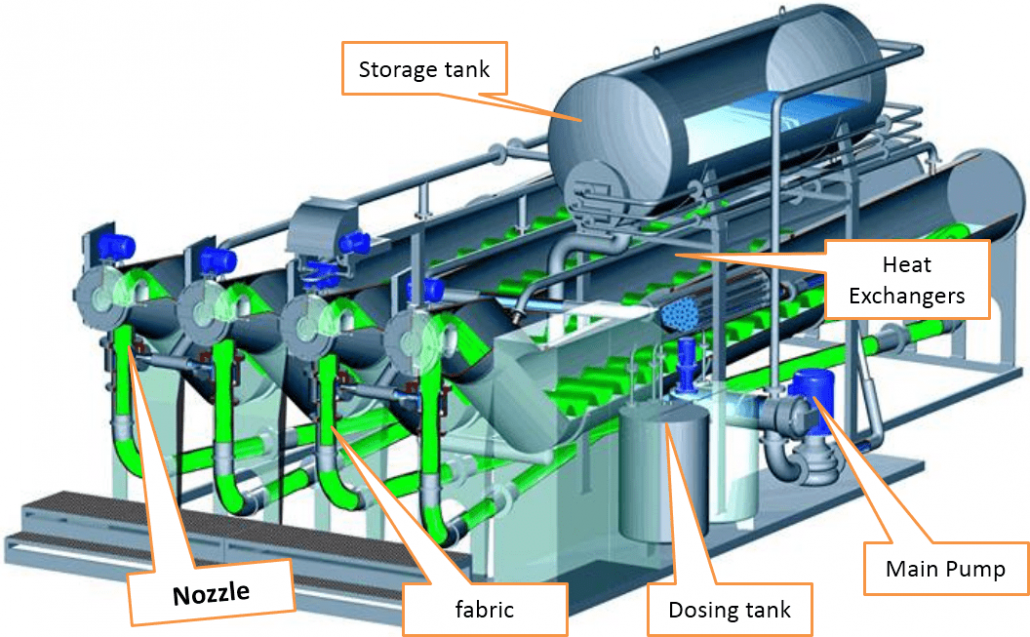
Jet Dyeing Machine (Moving Material and Moving Liquor)
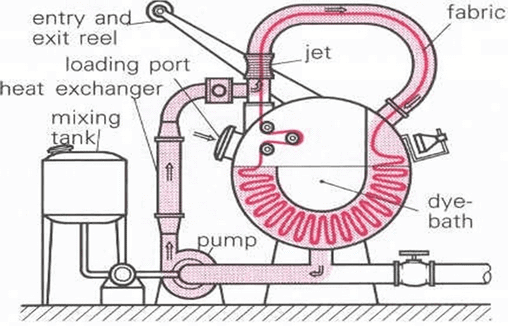
- It is similar to winch dyeing and fabric is processed in continuous loop. A typical cycle takes only 1 minute.
- This machine is used mostly to dye polyester fabrics as there are many disadvantages with HT winches which include long dyeing time.
- Fabric in rope form is carried forward by circulation of dye liquor jet & the fabric is fully tension less.
- Here substantial kinetic energy in the form of rapidly moving fluid is introduced in addition to the mechanical energy in the form of fabric transport so dyeing process is tremendously accelerated.
- Jet dyeing can usually be operated up to 140°C under high pressure.
- The cloth is moved along the tube at very high speeds (up to 400-600 m/min).
- Considerable amount of dye adsorption can occur when the fabric is going through the Venturi Tube which might take just 1 second. Dye diffusion takes place when the fabric is moving more slowly through the bottom of the machine in the remainder of the cycle which lasts about 1 minute.
How the turbulence of the liquor is created to transport the fabric along with it?
It’s based on Venturi tube.
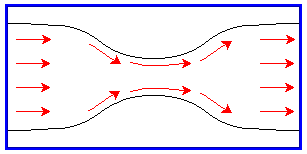
From Bernoulli’s equation we can arrive at the following conclusion –
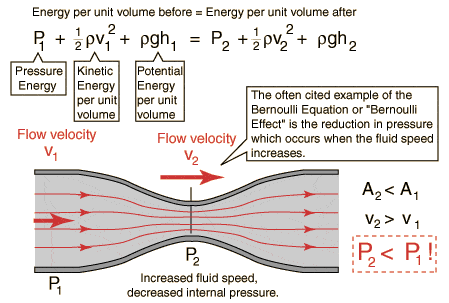
So, we can simply say –
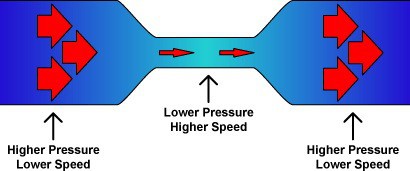
That narrow open end causes tremendous increase in speed of flow, forcing the fabric to move along with circulation of liquor. This also helps in dye penetration along with preventing the fabric from touching the walls of the tube.
You can see this video for further clarification.
What happens when the orifice of the Jet is too small or large & why accurate positioning of the Jet is important?
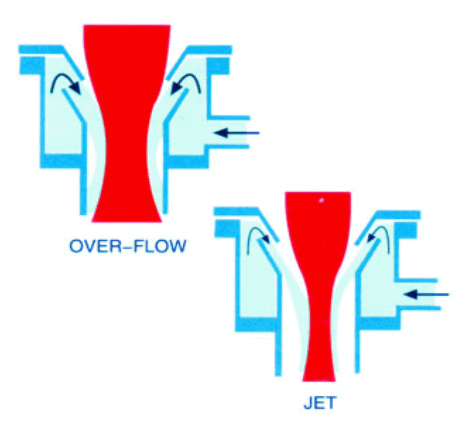
There are 3 types of Jet Dyeing machines, which are –
- Over flow dyeing machines
- Soft flow dyeing machines
- Air flow dyeing machines
I don’t have any intentions to make this article any longer so they won’t be discussed here.
Advantages of Jet Dyeing Machine
- Lower material to liquor ratio provides savings in energy & faster heating and cooling.
- Less lengthways tension & slightly fullness of handle.
- Vigorous circulation of liquor & material causes quicker dyeing.
- Frequent movement of fabric minimizes creasing problem.
- High fabric transport speed by adjusting nozzle valve to cause level dyeing.
- Less dye at the surface resulting in quicker washing with marginally better fastness properties.
Disadvantages of Jet Dyeing Machine
- Typical crease marks which might be developed during high temperature dyeing making it difficult to remove in finishing.
- High capital investment & maintenance costs.
- Limited accessibility to the material when the machine is running, the fabric is loaded & unloaded through a small port.
- Internal cleaning is difficult as the machine is completely enclosed. In particular, Polyester Oligomer deposits may develop on the hot surfaces & later dislodge. (Cleaning is done by circulating Caustic Soda or Sodium Dithionite).
- Any roughness inside the machine causing snagging of the fabric is difficult to locate.
- Vigorous movement of the liquor may create severe foaming.
- The force of the jet may damage delicate fabrics.
- Sampling of the dyed fabric during dyeing is difficult.
- Fabrics rom spun yarns of staple fibres may tend to become quite hairy in appearance because of abrasion.
REFERENCES
- Asim Kumar and Roy Choudhury, Textile Preparation and Dyeing, Oxford & IBH Publishing Co. Pvt. Ltd., 2006.
- Dr. V.A. Shenai, Technology of Dyeing, Eighth ed., vol. VI, Sevak Publications, 1997.
- E. R. Trotman, Dyeing and Chemical Technology of Textile Fibres, Charles Griffin & Company LTD, 2009.
- Arthur D Broadbent, Basic Principles of Textile Coloration, Society of Dyers and Colourists, 2014.
- Engr. Muksit Ahamed Chowdhury. (2013, 05 25). Dyeing Machines. Lecture Notes distributed at the Ahsanullah University of Science & Technology. Dhaka, Bangladesh.

